Have you ever wondered how your camera manages to take such beautiful pictures and videos? However, there is a significant magical process taking on inside; it involves more than merely pressing a button. Get ready to explore the fascinating world of pixels, microprocessors, and image perfection as we uncover the secrets of camera processors!

Have you ever thought about how a beautiful moment can be captured by hitting the shutter button? How does your camera set its focus on particular things? When a picture is taken then what happens inside the camera? Additionally, did you realize that videos are simply a collection of photos? Does every type of camera include a dedicated camera processor?
Let’s start an interesting exploration of the fundamental concepts of the camera.
Fundamental concepts
Pressing the Shutter: Capturing Time in an Instant
It’s like turning on a magical time-freezing machine when you hit the shutter button on your camera. The camera’s mechanism activates in that instant, recording an exact moment and keeping it for all time. It feels like you are saving a moment in time by turning it into a physical memory.

Focusing and Detecting Objectives: Sharpening the Details
Ever questioned how your camera determines what to focus on? Imagine the camera had a clever helper that could recognize objects and make sure they were visible and sharp. The camera analyzes the picture using complex algorithms and sensors to identify the primary subject, bringing it into crisp focus and making it stand out brilliantly.

Shutter Mechanism: Controlling the Flow of Light
The term “shutter” refers to an important element inside the camera that regulates how much light gets in. Imagine it as a magical portal that briefly opens when you click the shutter button. The foundation of the image you’ll record is formed using this opening, which enables light to travel and reach the camera’s sensor.

Transforming Light into Pixels
Let’s explore the fundamentals of how a camera takes a picture. The sensor is an extraordinary part found inside cameras. By absorbing the light that enters via the lens. then this sensor functions as a light-sensitive canvas. A digital image is made up of many small dots, or pixels. which are created as a result of the interaction of the light with the sensor. The image you see on the camera’s display is made up of these pixels.
Video: A Sequential Storytelling of Photos – Understanding fps
Videos are made by putting a series of photographs together, which is an interesting method of storytelling. Each picture is known as a frame and goes by quickly one after another.
which is creating the impression that you are turning through pages of a flipbook. Frames per second (fps), is a unit used to describe how quickly these frames are presented and what gives a video its smoothness and realism.
Processing and Storage
Complex algorithms and processes are present inside the camera and work their magic to improve and optimize the image that is obtained. These algorithms laboriously examine and improve the image, lowering noise, boosting colours, and ensuring the best result.
Once the image has been perfectly processed, it is saved in the camera’s memory and is available for you to enjoy and share with others.
How exactly do these amazing processors operate? Systems specifically created for image processing have been carefully constructed to handle the complex duties involved.
The camera processor enters the stage at that point.
The real use case of the camera processors (the system)
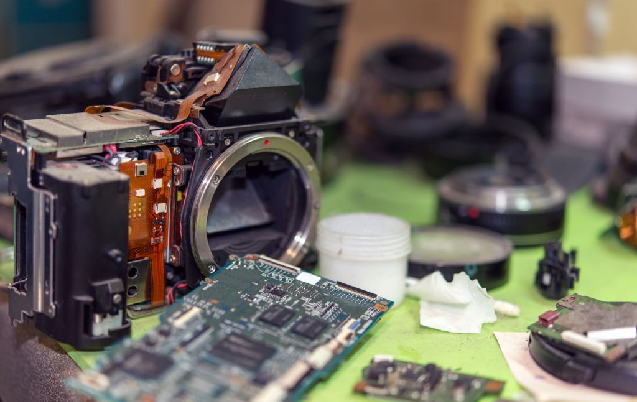

Image Processing Chip
When announcing their cameras, camera manufacturers like Sony, Canon, and Nikon frequently refer to particular image processing units. For instance, Canon uses DIGIC X, DIGIC 6+, and DIGIC 8, Sony uses BIONZ XR and BIONZ X, and Nikon uses Expeed 7 and Expeed 6.
These image-processing engines take care of things like image improvement, colour reproduction, and noise reduction.
A common misconception is that there is only one kind of camera processor. However, there is actually a wide range of additional camera processors, including AI processors.
Actually, the data sheet is not publicly available. company has their own secrets. However, a majority of these processors utilize the ARM architecture and employ Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) programming.
Additionally, they are primarily developed using the C language.
Sensor Controller
Sony cameras frequently use a separate chip that controls the picture sensor. This sensor controller controls important processes like exposure regulation, sensor readout, and other activities involving the image sensor.
Autofocus (AF) Chip
Dedicated AF chips may be found in cameras with advanced autofocus capabilities. This chip controls the autofocus system and analyses autofocus data to ensure precise and quick subject focusing.
Memory and Storage Controller
Cameras need memory and storage controllers to function. These controllers handle buffer management, data writing to memory cards, and other storage and Random Access Memory (RAM)-related operations.
Codec Chip
Cameras that can record video frequently have a codec chip specifically for that purpose. The encoding and decoding of video is handled by this chip. It decodes video streams for fluid playing and compresses video data for storage or transmission.
What is the programming language?
Software and firmware for Sony cameras are often developed using a variety of programming languages. Although Sony may not publicly share the precise programming language it uses internally to produce camera firmware, we may provide information on the most widely used languages in the sector.
For developing camera firmware, low-level languages like C and C++ are essential.
In order to connect directly with the hardware components of the camera, these languages offer the required tools and capabilities, assuring effective and optimum performance.
They let programmers directly manage a number of camera functionalities
It’s also important to highlight the specialized language Halide. A domain-specific language made especially for image processing jobs is called Halide. It enables programmers to explain complex image-processing algorithms clearly and effectively.
Halide is becoming more popular in the field of developing camera software because of its capacity to optimize and speed up image processing operations, while not being as widely used as C and C++.
What is the inside of these camera processors
let’s take a look at some examples
Sony BIONZ XR
The camera’s brain is a highly sophisticated system-on-chip (SoC) called the Sony BIONZ XR. This SoC makes use of ARM cores, a standard CPU architecture found in many different electronic gadgets. Both Linux and the AV real-time operating system (ITRON RTOS) are supported by the BIONZ XR. The camera can be operated effectively and dependably thanks to this software combination, which also offers sophisticated features and seamless image processing.
Canon DIGIC X
ASIC stands for an application-specific integrated circuit, and the Canon DIGIC X is an exclusive ASIC created only for Canon cameras. It is designed as an ASIC to carry out particular tasks and serve the purposes that Canon had in mind.
Canon emphasizes the benefits the DIGIC X delivers to their products rather than providing extensive technical details about it in the public domain.
Canon does not sell or grant licenses for the DIGIC X to other manufacturers, therefore they preserve the DIGIC X’s inner workings as their “secret sauce.”
This guarantees the exclusivity of their technology and offers them a market advantage. The DIGIC X, on the other hand, is based on the ARM instruction set and runs a proprietary software built on DryOS, which is Canon’s unique real-time operating system, according to information acquired by enthusiasts.
The sophisticated image processing skills and cutting-edge features present in Sony and Canon cameras are made possible by these camera processors’ cutting-edge architectures and operating systems.
The end product is a unique instrument that captures breathtaking photographs and enables photographers to unleash their creativity, despite the complexity of the technical aspects.
FPGA use in camera
A unique component known as an FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) may be operating silently in the background of some commercial cameras. FPGAs are adaptable programmable logic devices that provide flexibility and reconfigurability, making them beneficial in a variety of applications, including cameras.
Even while not all commercial cameras make use of FPGAs, there are some specialized situations where they are added for particular functions.
Let’s look at a few instances of commercial cameras that use FPGAs.these are another kind of camera processor.
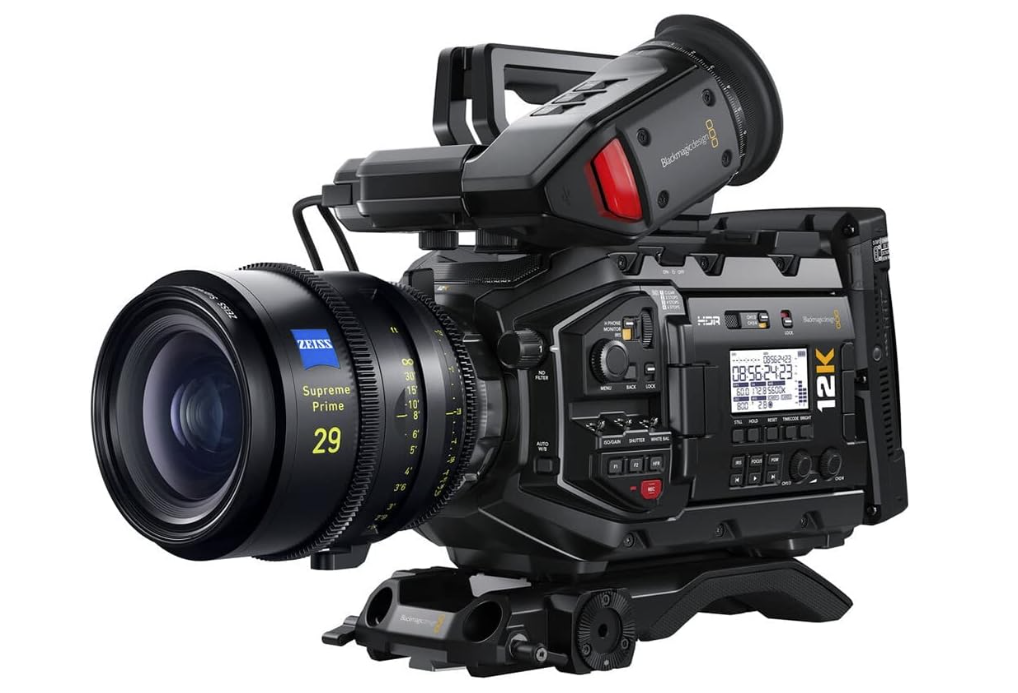
Blackmagic Design URSA Mini Pro
An FPGA is used by Blackmagic Design’s URSA Mini Pro professional digital cinema camera. Filmmakers can produce breathtaking images thanks to the camera’s high-speed processing and powerful video processing capabilities provided by this FPGA.
RED cameras
High-end cinema cameras from RED Digital Cinema, including the RED EPIC and RED RANGER series, are well known. To provide real-time processing and considerable control over image gathering and processing, these cameras frequently combine FPGAs. This enables cinematographers to produce results that are precise and vibrant.

Sony F65 CineAlta
A digital cinema camera called the Sony F65 CineAlta uses an FPGA to process images in real time. The camera can perform high-speed video capture, complex colour processing, and other advanced functions thanks to the FPGA. This enables filmmakers to produce engaging and visually stunning movie experiences.

Phantom high-speed cameras
High-speed cameras are a speciality of Vision Research, including the well-liked Phantom series. These cameras are used in industrial settings, scientific research, and sports analysis.
In order to accomplish high-speed data processing and superior image capabilities, FPGAs are frequently included in these cameras.
This makes it possible for experts, researchers, and scientists to precisely record and evaluate rapid-fire events.
These cameras can effectively interpret and manipulate data in real time by using FPGAs, which results in improved performance and cutting-edge functionality.

Despite the complexity of the technical aspects of FPGA implementation, the inclusion of these devices in cameras guarantees better image quality, processing speed, and control.
FPGAs are another kind of advanced camera processor.
Summary
Several activities work together inside a camera’s image processor to process the image data that is collected. The processor’s primary responsibilities include managing the image sensor, taking digital information out of pixels, and demosaicing full-colour data to recreate it. The processor uses noise reduction techniques, makes adjustments to the white balance, colour, and exposure parameters, and optimizes brightness and dynamic range.
Additionally, the image processor conducts localized modifications, sharpening, and compression for cameras that enable it. Additionally, it aids with autofocus, subject tracking, and image stabilization, which reduces camera shake. The processor also provides specialized modes and features like panoramic stitching, HDR imagery, and artistic filters, allowing photographers to capture distinctive viewpoints and unleash their creativity.
By combining these features, the image processor creates gorgeous photos from raw data, showing the technical skill that enables photographers to capture their priceless moments with accuracy and creative flair. Different camera models and manufacturers use their own exclusive processing methods and algorithms to stand out in the market, illuminating the fascinating complexity that works in the background.


I have been surfing online more than 3 hours today yet I never found any interesting article like yours It is pretty worth enough for me In my opinion if all web owners and bloggers made good content as you did the web will be much more useful than ever before
Wow amazing blog layout How long have you been blogging for you made blogging look easy The overall look of your web site is magnificent as well as the content
The articles you write help me a lot and I like the topic
Your articles are extremely helpful to me. May I ask for more information?
May I request that you elaborate on that? Your posts have been extremely helpful to me. Thank you!
Excellent website. Plenty of useful information here. I’m sending it to a few friends ans also sharing in delicious. And of course, thanks for your effort!
Greetings! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and say I truly enjoy reading through your posts. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that cover the same subjects? Thank you so much!